Listen above to an audio version of Why PETA Kills, my book, which tells the story of Maya and those of over 30,000 other animals PETA has put to death.
On October 18, you can also download the e-book from Amazon for free. (Ignore Kindle Unlimited and click below where it says “$0.00 to buy.”)
On October 18, 2014, two PETA representatives backed their van up to a home in Parksley, VA, and threw biscuits to Maya, who was sitting on her porch. They hoped to coax her off her property and allow PETA to claim she was a stray dog “at large” whom they could legally impound.
Maya refused to stay off the property and, after grabbing the biscuit, ran back to the safety of her porch. One of the PETA representatives went onto the property and took Maya. Within hours, Maya was dead, illegally killed with a lethal dose of poison.
A PETA spokesperson claimed Maya was killed by “mistake,” and defying credulity, explained that the same PETA representative who had earlier sat on the porch with Maya’s family talking to them about her care and who was filmed taking Maya from that same porch mistook her for a different dog. The “apology” was not only a devastating admission of guilt but evidence that killing healthy animals was business as usual for PETA employees — so commonplace that the only excuse PETA could offer for Maya’s death was that in taking her life, a PETA representative had mistaken her for another healthy animal they had decided to kill. Was it likewise a “mistake” that five other animals ended up dead from the same trailer park and on the same day, too?
Though PETA claimed to be “devastated” by Maya’s death, the claim was contradicted by the facts and, given its timing, motivated not by honesty, transparency, or genuine contrition but by political necessity as the Virginia Department of Agriculture had opened an investigation into Maya’s killing and Virginia’s governor was weighing whether to sign into law a bill overwhelmingly passed by the legislature aimed at protecting animals from PETA.
As public outrage over PETA’s killing of Maya spread, a former PETA employee came forward, shedding even more light on how disingenuous PETA’s claim of being devastated at the killing of Maya was. Explaining that killing healthy animals at PETA was not an anomaly but “standard operating procedure,” Heather Harper-Troje, a one-time PETA field worker, publicly uncovered the inner workings at PETA as no former employee ever had. “I know from firsthand experience that the PETA leadership has no problem lying,” she wrote. “I was told regularly to say whatever I had to say in order to get people to surrender animals to me, lying was not only acceptable, it was encouraged.” The purpose of acquiring these animals, according to Harper-Troje, was “to euthanize the[m] immediately.”
Maya’s family would ultimately sue PETA, alleging conversion of their dog (theft), trespass, and intentional infliction of emotional distress. PETA, in turn, asked the court to throw out the lawsuit based on several questionable claims.
First, PETA argued that Maya was legally worthless because she was not licensed, citing an 1887 law that required a dog “to be properly licensed as a condition of being deemed personal property.” Putting aside the irony of a supposed “animal rights” group arguing that Maya had no value, the statute they cited was repealed in 1966. It had not been the law in half a century.
Alternatively, PETA argued that Maya had no value beyond the replacement cost for another dog. In other words, PETA’s position was that Maya was like a toaster. If you break it, you throw it away and get a new one.
Third, PETA argued that they had permission to enter the trailer park from its owner to remove community cats, so they cannot be guilty of trespassing for entering a private residence in that trailer park to kill a family’s dog.
Fourth, PETA argued that the theft and killing of Maya was not “outrageous,” a prerequisite to the awarding of punitive damages.
Finally, in an argument reeking with racist overtones, PETA demanded to know if Maya’s family was legally in the U.S.
After arguing and losing most of the pre-trial motions — including rulings that the family’s immigration status was not relevant to the theft and killing of their dog and that such conduct was, indeed, “outrageous” — as well as facing the specter of being forced to turn over records and testify under oath about PETA’s inner workings, and perhaps trying to put the publicity behind their killing of Maya behind them, PETA settled the case, paying Maya’s family $49,000.
But the condemnation only grew following a series of articles I wrote about Maya’s killing, which ultimately led to the publication of Why PETA Kills, my book. Why PETA Kills tells Maya’s story and that of over 30,000 others who have also died at their hands, a number that continues to increase by the thousands every year. In 2022, for example, PETA put to death 1,374 out of 1,737 cats. Another 347 went to pounds that also kill animals. Historically, many of the kittens and cats PETA has taken to those pounds have been killed, often within minutes, despite being young (as young as six weeks old) and healthy.
Not only do those records prove the lie that all of the animals PETA rounds up to kill are “suffering,” but if those cats and kittens were killed or displaced others who were killed, that puts the overall cat death rate as high as 99%. They only adopted out 15 cats, an adoption rate of ½ of 1% despite millions of “animal loving” supporters, a staff of hundreds, and revenues in excess of $72 million.

While dogs fared a little better, 718 out of 1,041 were killed. Roughly 4% were adopted out. And PETA staff also killed almost 80% of other animal companions: 30 out of 38.
To date, PETA has killed 46,364 dogs and cats and sent thousands more to be killed at local pounds, that we know of. The number may be many times higher. According to Harper-Troje,
I was told regularly to not enter animals into the log, or to euthanize off-site in order to prevent animals from even entering the building. I was told regularly to greatly overestimate the weight of animals whose euthanasia we recorded, in order to account for what would have otherwise been missing ‘blue juice’ (the chemical used to euthanize); because that allowed us to euthanize animals off the books.
Following the release of Why PETA Kills, PETA filed a run-of-the-mill defamation lawsuit targeting The No Kill Advocacy Center (NKAC), my organization, and me in an attempt to intimidate me and others into silence. But they didn’t sue me directly, as they knew it would ultimately fail: truth, after all, is a defense to defamation. More importantly, they feared doing so as suing me would be dangerous for PETA. Not only would it allow me to force the deposition (e.g., testimony under penalty of perjury) of Ingrid Newkirk, the architect of PETA’s killing, as well as others at PETA who do the actual killing, but it would allow me to seek documents from PETA that would augment what public records and the PETA employees I spoke with already revealed: that PETA intentionally seeks out animals to kill and that the majority of those animals are healthy and adoptable. Absent a court case, as a private organization, PETA is not required to release that information under state freedom of information laws and has ignored my requests to do so.
Instead, PETA named me as a “co-conspirator” but not as a defendant in the complaint, a procedural gimmick that gave PETA the ability to issue a subpoena to (try to) seek the names of PETA employees who, fearing retribution, spoke to me on condition of anonymity; information that was used to corroborate newspaper articles, on the record sources, government documents, testimony and information from civil and criminal cases against PETA, videotape evidence, and admissions of killing by PETA officials. At the same time, that procedural ploy would prevent me from demanding documents and depositions of PETA leadership and staff in return.
But PETA’s legal tactic failed to take into account two important factors. First, I would never reveal my confidential informants. Second, I did not have to legally do so, given my First Amendment rights as a journalist. In an attempt to force me to, however, PETA filed a motion in court to compel the disclosure of the names, claiming that as an animal advocate, I was not entitled to the protection of the First Amendment, a point of view they hypocritically reject for themselves and which, the Reporters Committee for Freedom of the Press, the organization founded to protect the rights of journalists by legendary Washington Post editor Ben Bradlee of Pentagon Papers fame, called “alarming.”
In assisting me with my legal defense, the Reporters Committee noted,
We’re concerned about the legal efforts to require Nathan Winograd to reveal the confidential sources for his reporting on PETA’s practices. Both the First Amendment and California’s constitution protect those who engage in journalistic activity… and any efforts to limit these protections should be alarming for all newsgatherers.
Threatened with a fine and jail time if I refused to reveal my sources, my lawyer argued that California Courts have consistently ruled that the First Amendment protects “investigative reporting.” And investigative reporting includes “authors such as Lincoln Steffens and Upton Sinclair [who] exposed widespread corruption and abuse in American life. More recently, social critics such as Rachel Carson, Ralph Nader, Jessica Mitford, and others have written books that have made significant contributions to the public discourse on major issues confronting the American people.”
As my attorney argued,
Every crusading journalist in that pantheon of heroes cited by the court would have flunked PETA’s putative ‘journalism’ test, for their journalism was inseparable from their advocacy. Indeed, Sinclair and Nader took their advocacy onto the campaign trail and sought public office. Winograd and NKAC’s intertwined investigative and advocacy work are no different from that done by Nader and his nonprofit Public Citizen.
The court agreed. Despite PETA hiring one of the most expensive law firms in the world, the Court denied PETA’s motion, not only providing me and, more importantly, the animals an important victory but breaking new ground by extending First Amendment protections to new/non-traditional media.
Following that ruling, another whistleblower from inside PETA openly came forward and confirmed what my sources had revealed: that PETA staff lie to people to acquire their animals to kill, kill despite adoption alternatives, and indoctrinate people to kill in a cult-like atmosphere she described as “terrifying.”
[A]s most new PETA employees are blooming animal rights activists, freshly plucked from college and determined to do whatever it takes to succeed in this demanding, low-paying activist world, PETA’s methodology of indoctrination is quite successful. These employees soak it all in like a sponge, as I did at the age of 21 when I started there, and begin to spout the organization’s soundbites at every turn. They will start to do so so naturally that they can’t see where they themselves end and the organization begins.
“Ultimately,” wrote Laura Lee Cascada, a PETA field worker whose job included rounding up animals to kill, “the culture was terrifying and desensitizing — and I gradually felt that my view of death, of taking animals’ lives, was being warped, my emotions being stripped away.”
Like Heather Harper-Troje before her, Cascada’s chilling account described the method whereby employees are intimidated and emotionally manipulated into participating in the killing of animals, an act that came to be euphemistically called to “take care of” an animal (the words “killing” and even “euthanasia” are not used). Employees “were forced to participate in euthanasias they didn’t believe in” or “were fired because they refused to do so.”
[I]f an employee, like many animal rights advocates who believe in the rights and autonomy of each individual animal, wanted to critically assess whether a euthanasia decision was truly the best thing for an individual animal in his or her unique circumstances, there was a real, true fear of being branded as an advocate for hoarding or a secret supporter of the enemy. Thus, speaking up could have meant being booted from the tribe.
Cascada also described numerous examples of healthy animals who were killed for the “good of all animals”:
I rescued and cared for a pair of birds from a cruelty case for weeks, bonding with and growing to love them. When the decision was made to euthanize the boy because of a debilitating medical condition, the girl was also euthanized because it was thought that she would be lonely without him. She was one of those lumped into the ‘unadoptable’ category PETA brushes past as it explains its euthanasia statistics each year. I was expected and required to swallow my emotions for her for the good of all animals. I was expected to welcome her death as a positive outcome in order to maintain my employment.
Another time, I rescued an unloved dog whose body condition and personality were unremarkable, meaning there was no immediate indication for euthanasia. I quickly heard from my mom that she’d be interested in adopting him. I excitedly emailed the manager of the shelter to make this offer but never received a reply. A few days later, I checked in with her and was told that he had already been killed.
She recounted being told to lie to people to acquire animals to kill and getting chastised for trying to find them homes. For example, Cascada wrote that she,
[R]esponded to a call from a concerned woman who’d found an abandoned days-old kitten under her porch. When I came to pick up the kitten, I had her sign a generic give-up form that spelled out that euthanasia was a possibility. But I was instructed to repeatedly convey that we would do our absolute best, and so that’s what I said, even as the woman described her careful search for an organization she knew would work around the clock to help this tiny being pull through. It was my job to make sure I did not leave without that cat — that I said whatever necessary for the woman not to change her mind.
The entire way back to PETA’s Norfolk, Virginia, headquarters, I sobbed, petting the infant cat in my lap, telling her things would all be OK, even though in my gut I knew it wouldn’t, that she never really had a chance. I even began plotting out how I might take a detour and deliver her to a rehabber instead. But how could I explain a missing kitten to the woman waiting with the needle? I couldn’t, so I complied without a word.
As a result of coming forward, she reported that she was,
[C]ontacted by individuals from all over the country expressing their gratitude, and their own fear, about speaking out about their experiences. People who worked at PETA and were forced to lie about euthanasias, people who were forced to euthanize animals they loved as a condition of their employment, and people who were told by leadership that they were worthless. There are dozens, and maybe hundreds, of us. Most are still afraid to break their silence.
PETA’s lawsuit would ultimately collapse, but four important things came out of my victory against them. First, as noted above, it extended First Amendment protections for investigative journalism to new media for the first time.
Second, it demonstrated that PETA may have deep pockets and has no qualms about misusing the court system in an attempt to intimidate people into silence, but their strategy will always be limited by the fact that depositions and the witness stand could compel employees, including Newkirk, to testify under penalty of perjury. Consistent with the overwhelming evidence already available, such testimony would be damning, and PETA knows it. If people stand up to PETA’s donor-funded intimidation tactics rather than cower to them, PETA will invariably back down.
Third, their empty saber rattling may have led to another whistleblower openly coming forward.
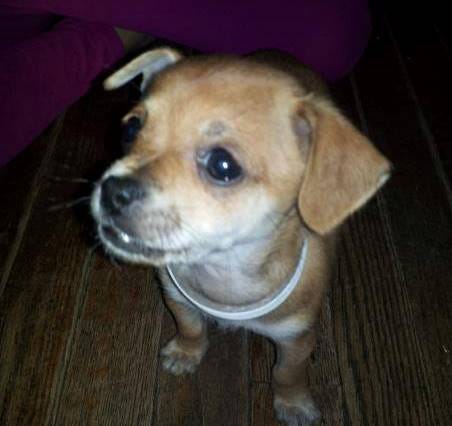
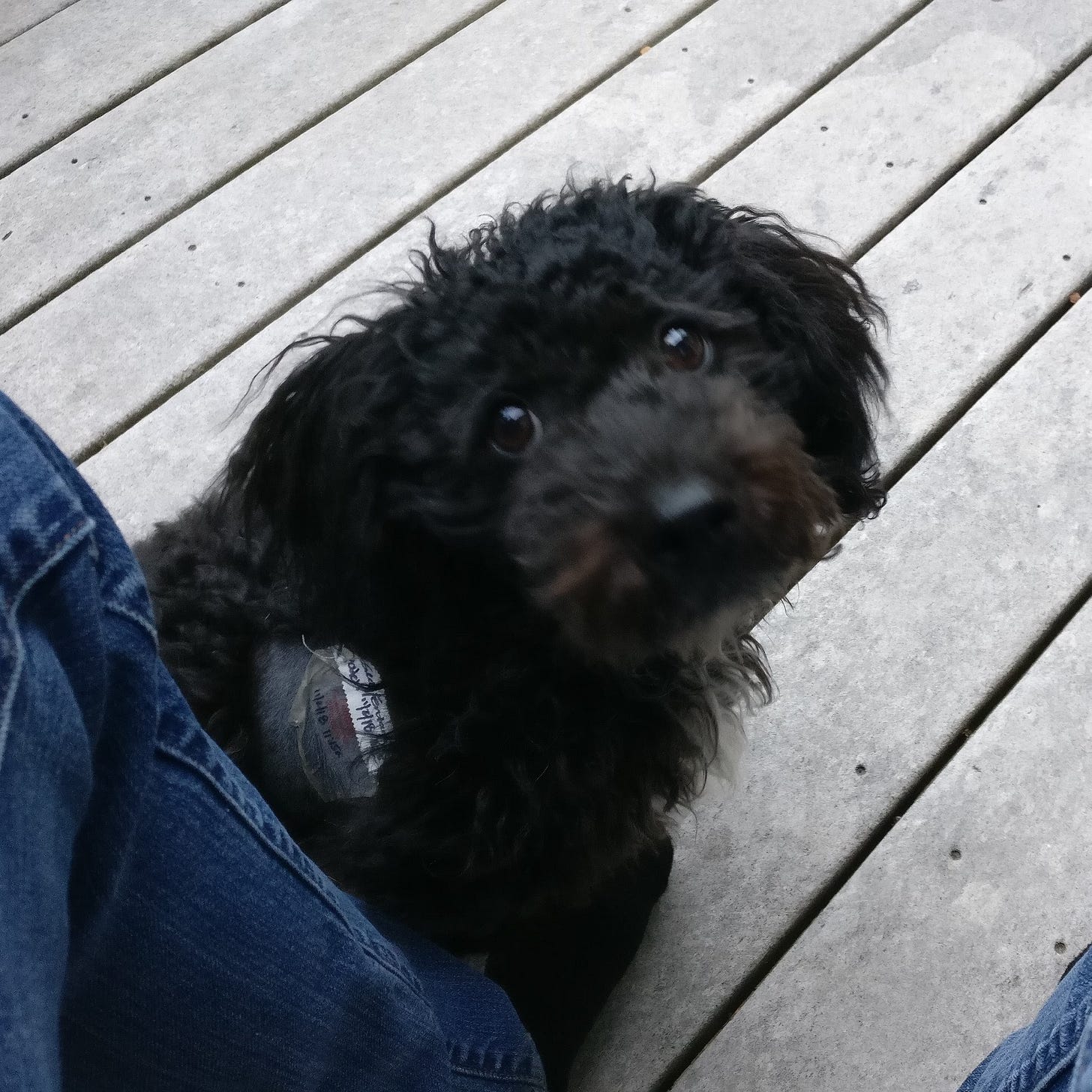
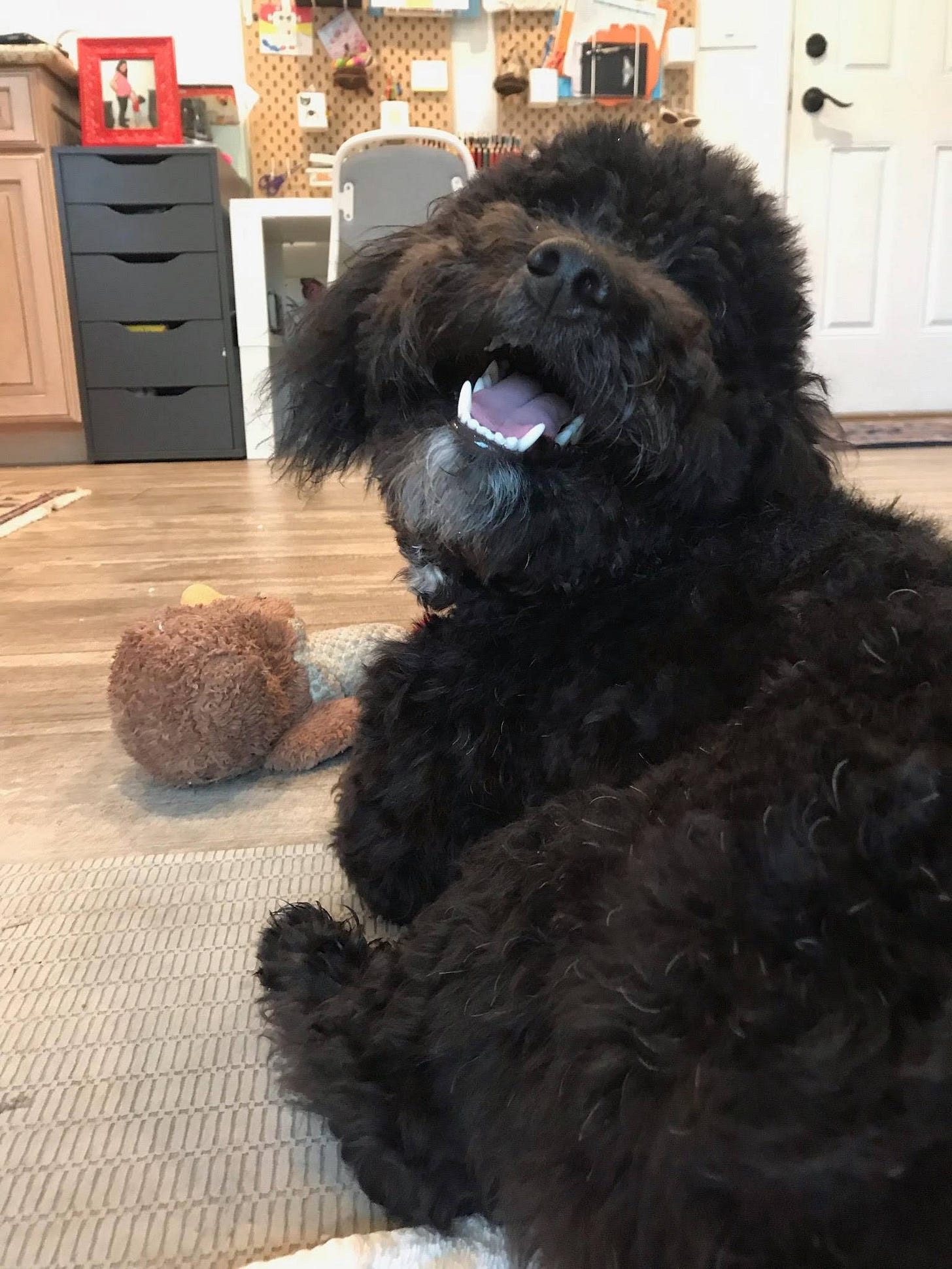
Fourth and finally, it led me to Ralph.
As fate would have it, on the way to court in the case, my wife and I came upon a little dog who had been hit by a car, bleeding in the gutter. Wrapping him in a coat, we rushed him to the nearest emergency veterinary hospital, where he was given the care he needed, including pain medication.
After recovering from his injuries at our house, we found him a loving, new home consistent with our belief in the ethical treatment of animals. Were it not for PETA’s meritless lawsuit, we would never have found him.
For obvious reasons, I am grateful that it was us and not PETA representatives who saw him on the way to the courthouse. If PETA had gotten to him and history is any guide, Ralph would no longer be alive, put to death with a lethal dose of poison.
Because despite all we may still not know about PETA, this much is certain: PETA is letting loose upon the world individuals who not only believe that killing is a good thing and that the living want to die but who are legally armed with lethal drugs that they have already proven — over 46,000 times — that they are not averse to using.